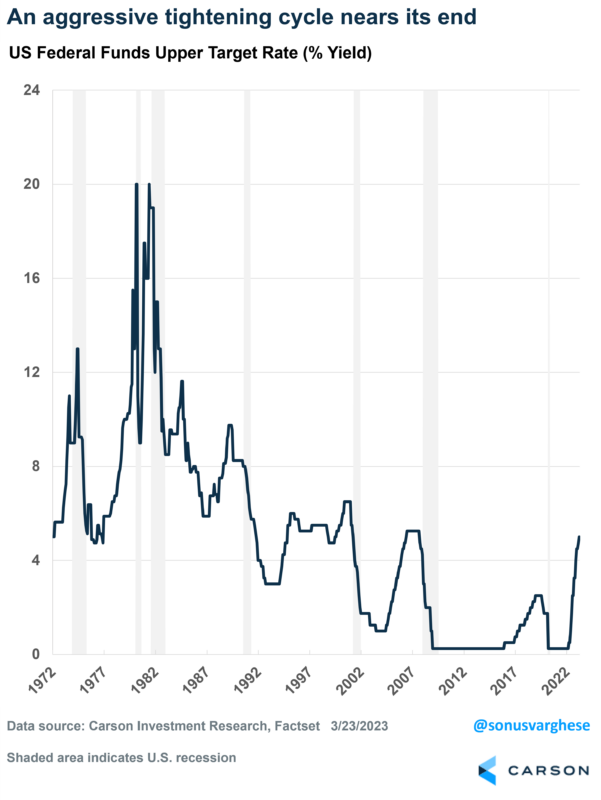
The Federal Reserve raised the federal funds rate by 0.25% at their March meeting, bringing it to the 4.75-5.0% range. This is the ninth-straight rate increase and brings rates to their highest level since 2007. However, the most aggressive tightening cycle since the early 1980s, which saw them lift rates all the way from near zero to almost 5%, is near its end.
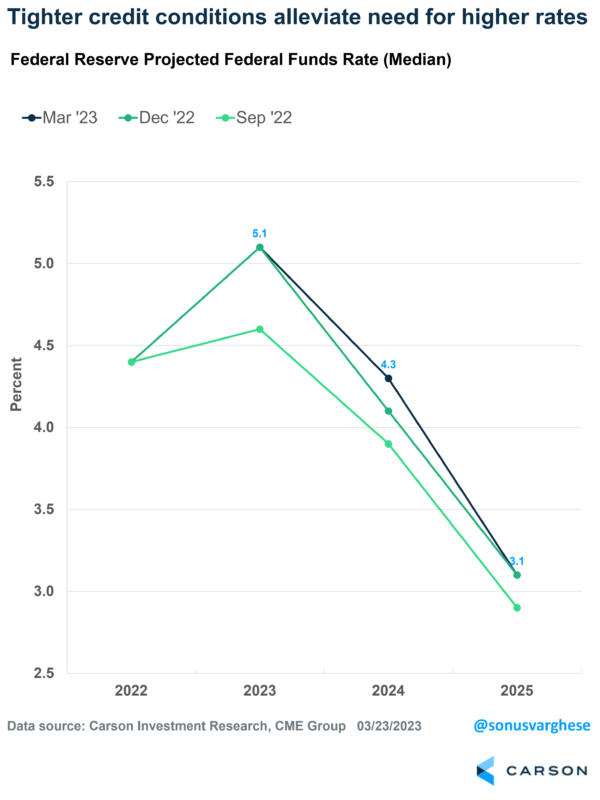
Up until early February, Fed officials expected to raise rates to a maximum of about 5.1% and hold it there for a while. However, since that time, we’ve gotten a slew of strong economic data, including elevated inflation numbers. This pushed fed officials to give “guidance” that they expected to raise rates by more than they estimated back in December.
Market expectations for policy also moved in conjunction. Prior to February, markets expected the Fed to raise rates to 5% by June, and subsequently lower them by about 0.5% by the end of the year. But strong incoming data and Fed guidance pushed expectations higher, with the terminal rate moving up to 5.6% and no cuts in 2023.
The Silicon Valley Bank crisis changed everything
The bank crisis that erupted over the last couple of weeks resulted in a significant shift, both in expectations for policy and now the Fed as well. See here for our complete rundown on SVB and the ensuing crisis.
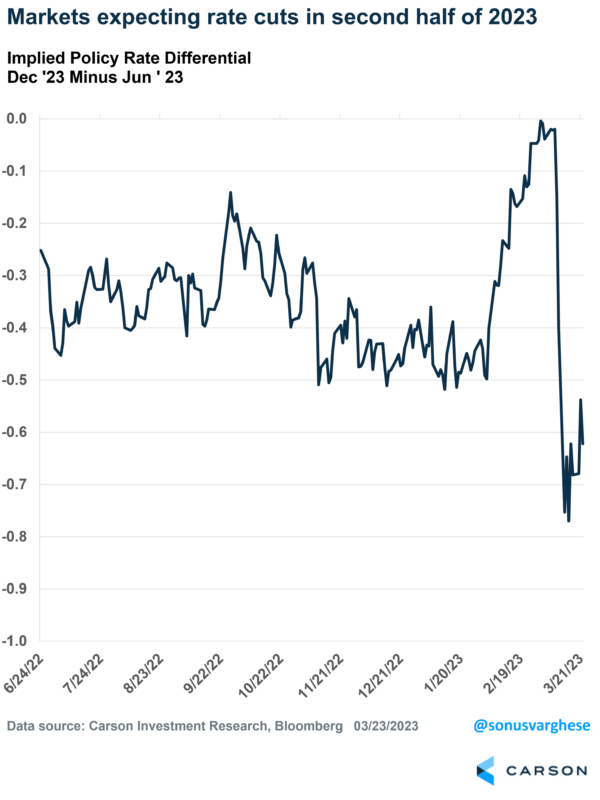
Market expectations for Fed policy rates immediately moved lower. Markets expected the stress in banks to translate to tighter credit conditions, which in turn would lead to slower economic growth and lower inflation.
This was nicely articulated by Professor Jeremey Siegel, one of the foremost commentators on financial markets and fed policy, in our latest episode of the Facts vs Feelings podcast, Prof. Siegel said that tighter credit conditions, as lending standards become more strict, are de facto rate hikes.
Fed Chair Powell more or less said exactly the same thing after the Fed’s March meeting. The 0.25% increase was an attempt to thread the needle between financial stability and fighting inflation. Fed officials also forecast the fed funds rate to hit a maximum of 5.1%, unchanged from their December estimate. This is a marked shift from what was expected just a few weeks ago, with Powell explicitly saying that tighter credit conditions “substitute” for rate hikes.
There’s a lot of uncertainty ahead
While the recent bank stresses are expected to tighten credit conditions and thereby impact economic growth and inflation, there are a couple of open questions:
- How big will the impact be?
- How long will the impact last?
These are unknown currently. Which means future policy is also unknown.
Fed officials expect to take rates to 5.1%, i.e., one more rate increase. And then expect to hold it there through the end of the year. In short, they don’t expect rate cuts this year.
Yet investors expect no more rate increases and about 0.6% of rate cuts in the second half of 2023. Markets expect the policy rate in June to be at 4.8%, while expectations for December are at 4.2%.
There’s clearly a huge gulf between what the Fed expects versus what investors expect. This will have to reconcile in one of two ways:
- Market expectations move higher – if economic/inflation data remain strong and credit conditions don’t look to be tightening significantly.
- Fed expectations move lower – if the banking sector comes under renewed stress, credit conditions could tighten significantly and eventually lead to weaker data.
Things are obviously not going to go in either direction in a straight line. It’s going to be a bumpy ride as new data points come in, not to mention news/rumors of renewed problems in the banking sector.